Home > Archives for James Bradford >
A Guide To Fire Alarm Testing Regulations
To prevent your business premises from becoming part of such sad statistics, it’s crucial that you properly maintain your fire alarms and test them regularly. But what are the fire alarm testing regulations? And what is the right fire alarm testing frequency?
Is a Fire Alarm a Legal Requirement?
England, Wales, Scotland, and Northern Ireland all have different legal requirements for fire alarms. Each country’s regulations detail differing levels of protection, but is a fire alarm a legal requirement? In short, the answer is yes:
- In England and Wales, fire safety legislation falls under The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005;
- Scotland’s regulations fall under Part 3 of The Fire (Scotland) Act 2005;
- Northern Ireland’s laws come under The Fire Safety Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2010.
Anyone who controls a building, such as an employer, managing agent or building owner, or even a tenant, is a “responsible person” and must ensure adherence to the required fire safety regulations relevant to their premises.
A responsible person must ensure a suitable fire detection and warning system is in place, and that the system gets tested correctly and regularly.
Fire Alarm Testing Regulations
If you are the person responsible for maintaining fire alarm systems at your premises, you’ll need to adhere to all appropriate fire alarm testing legal requirements. In the context of testing, you need to know how to test your fire alarm and how often.
Fire Alarm Testing Frequency
At a minimum, you must legally conduct six monthly inspections of your fire alarm system each year. When it comes to testing your fire alarms, the fire alarm testing frequency demanded by law is weekly.
For properties in England and Wales, the legislation covering fire alarm testing is Article 17 of The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005.
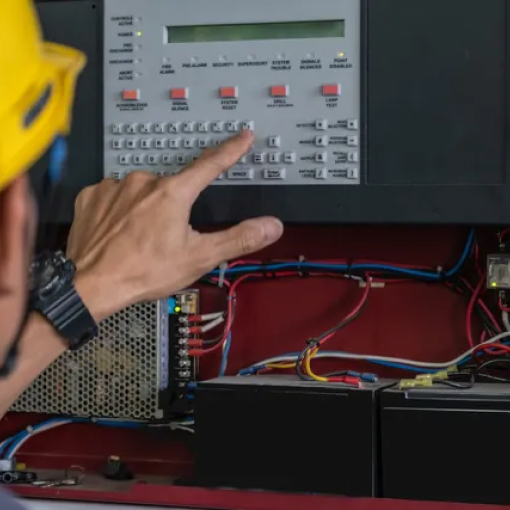
How to Test a Fire Alarm
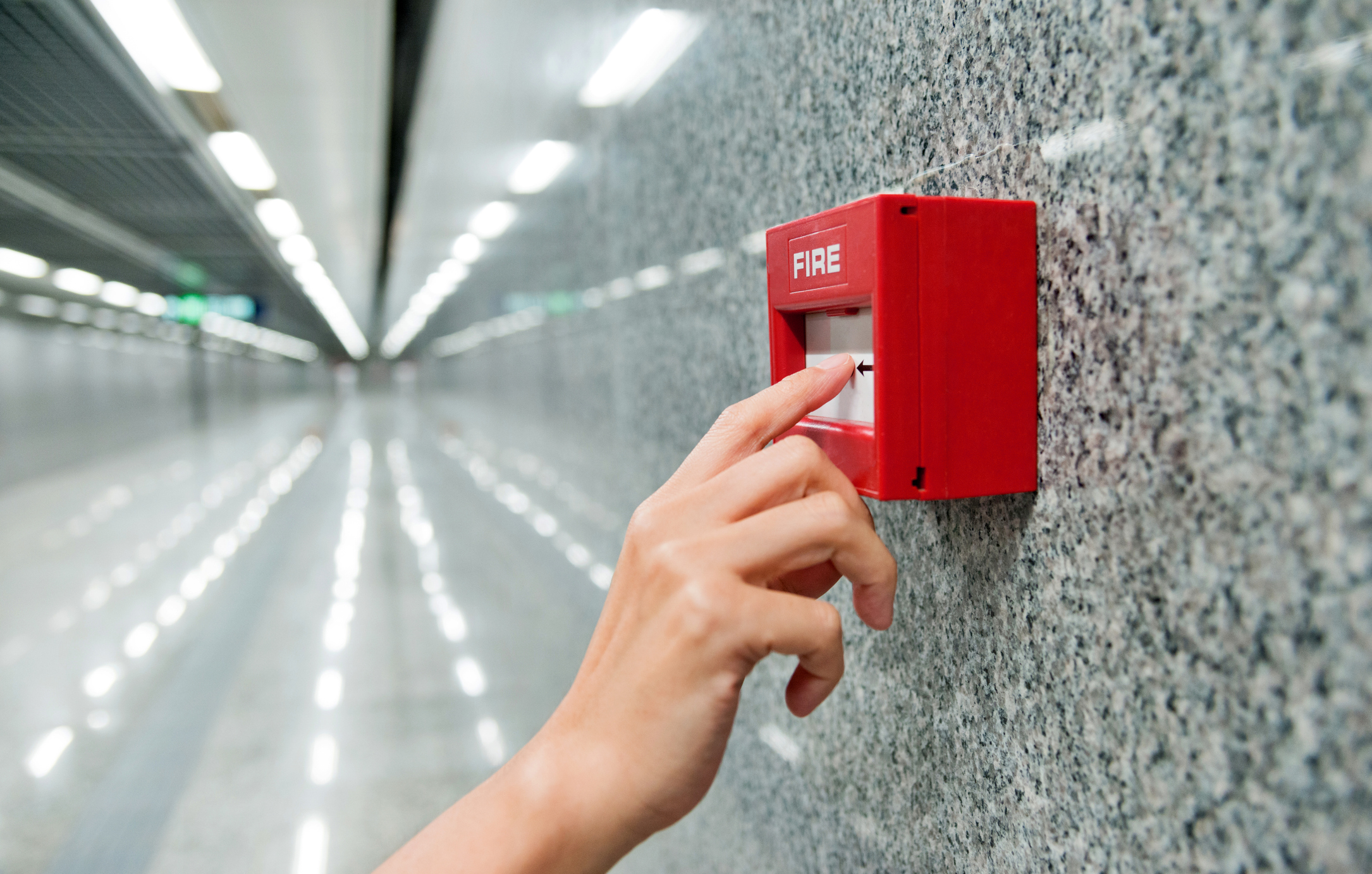
Fire alarm tests are necessary for two reasons. Firstly, it ensures the system is fully operational. And secondly, people in your building, such as employees, are familiar with how the fire alarm sounds.
Fire alarm systems can differ depending on the make and model, and the type of building they protect. But, the general procedure is as follows:
- Inform all people in the building of an imminent fire alarm test;
- Check the alarm control panel has a valid connection to the ARC (alarm receiving centre) and put it into ‘test’ mode;
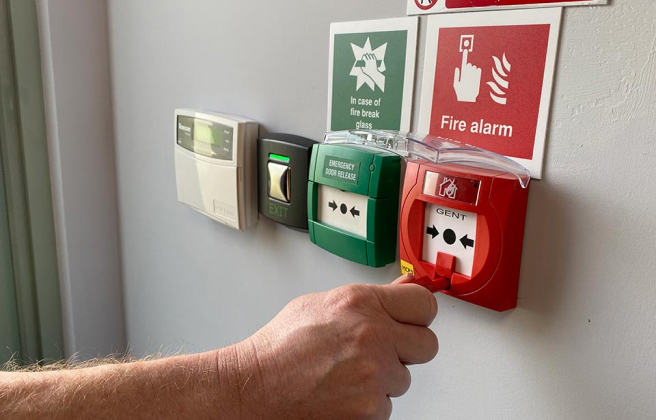
- Have a manual call point key on you, as you’ll need it to reset the system;
- Activate a manual call point, wait for the alarm sounders, and use the key to reset it;
- Go back to the alarm control panel, verify the manual call point location is correct, and then silence the alarm sounders;
- Write down the results of your fire alarm test in your fire logbook;
- Contact the ARC and confirm they’ve received your fire signal;
- Reset the alarm control panel and take it out of test mode.
How Britannia Can Help
Britannia Fire & Security is one of the UK’s biggest suppliers, installers, and maintainers of commercial fire alarm systems. We can ensure that your premises have a fully-functional alarm system that meets your needs and legal obligations.
Contact us today at 01733 246990 to find out how we can help your business stay safe.