What Fire Extinguisher Should Not Be Used in Confined Spaces?
Which Type of Fire Extinguisher Shouldn’t Be Used in a Confined Space?
When considering the type of fire extinguisher to use in confined spaces, the choice depends greatly on the fire’s nature and the area’s characteristics. Two specific types of fire extinguishers are generally advised against in such settings: carbon dioxide fire extinguishers and dry powder fire extinguishers. These types possess characteristics that can pose significant risks in enclosed environments.
Carbon Dioxide Fire Extinguishers
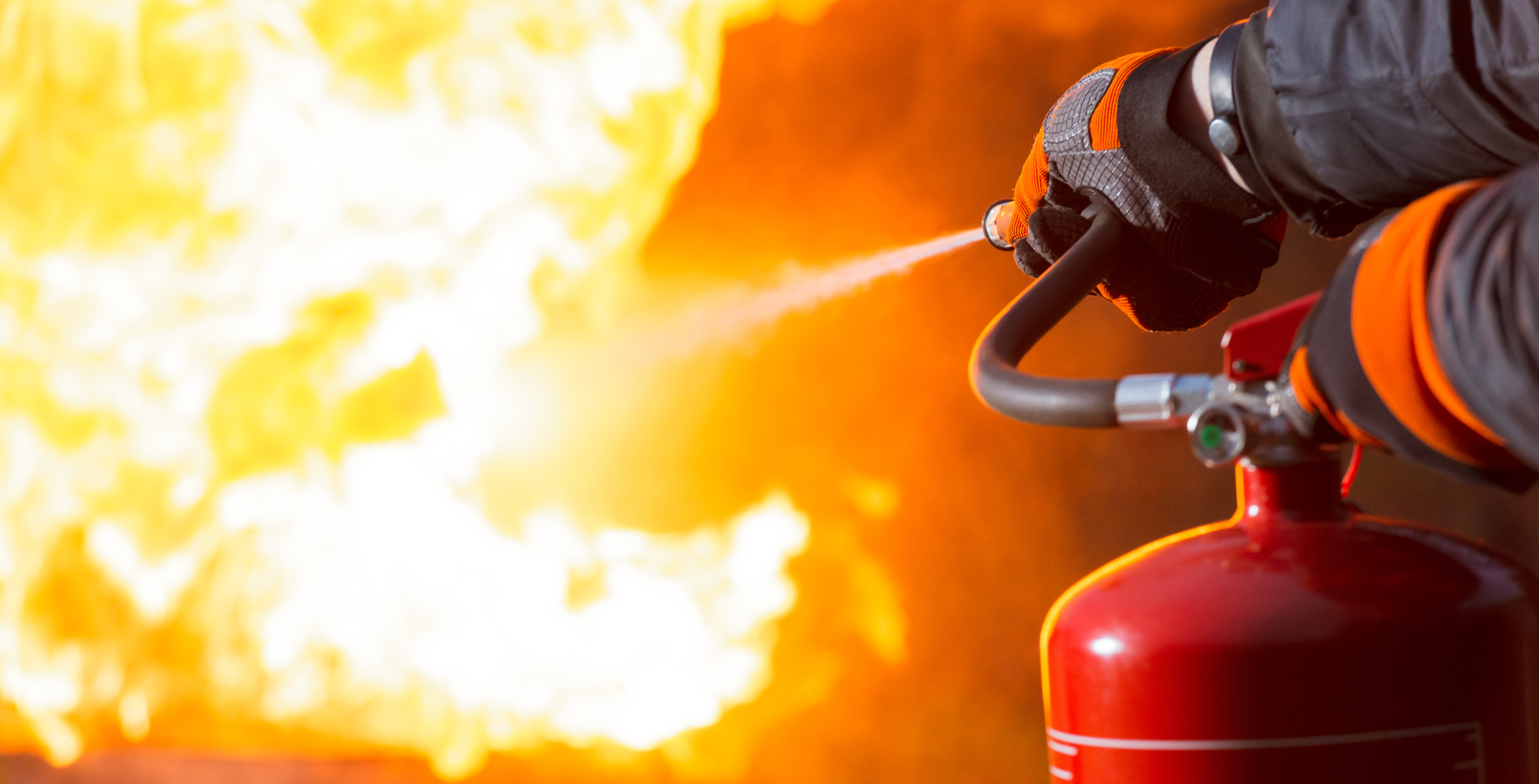
Carbon dioxide (CO2) fire extinguishers are known for their effectiveness in extinguishing electrical fires and those involving flammable liquids. But, they’re not suitable for use in confined spaces. The primary concern with CO2 extinguishers is that they displace oxygen as they release carbon dioxide gas to smother the fire. In an enclosed area, this rapid displacement can create an asphyxiation hazard, lowering the oxygen levels to a point that can be dangerous for any person present.
Dry Powder Fire Extinguishers
Dry powder fire extinguishers are versatile units capable of tackling Class A, B, and C fires, making them suitable for various situations. However, their use in confined spaces is problematic for several reasons. First, the powder can reduce visibility when discharged, which is especially dangerous in an already limited space where escape routes must be clear.
Second, the inhalation risk associated with the fine powder is significant. It can cause respiratory distress or exacerbate existing conditions such as asthma or lung problems. This factor alone makes dry powder extinguishers a poor choice for confined environments, where ventilation is limited and the powder can remain suspended in the air for a longer period.
Understanding the Class of Fire
Identifying the class of fire is key when selecting the appropriate fire extinguisher, especially in confined spaces. The classes of fires include:
- Class A – Fires involving solid materials such as wood, paper, or textiles.
- Class B – Fires involving flammable liquids like petrol, diesel, or oils.
- Class C – Fires involving gases.
- Class D – Fires involving metals.
- Class E – Fires involving live electrical apparatus.
Each class of fire requires a specific type of extinguisher that can safely and effectively put out the fire without worsening the situation. In confined spaces, where escape routes are limited and the environment can change rapidly, choosing the correct extinguisher is not just a matter of efficacy but also of safety.
Under the Confined Spaces Regulations (1997) and the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations (1999), it’s a legal requirement that all employees working in such conditions are trained to recognise these dangers and know how to respond appropriately in emergency situations. This training helps prevent accidents and ensure safety during fire emergencies in confined spaces.