Who’s Responsible for Enforcing Fire Legislation?
Who is Responsible for Fire Safety?
The regulatory Fire and Safety Order (RFSO) applies to premises in England and Wales, but not Scotland or Northern Ireland. The order is enforced by the fire and rescue authority in England, and by the Scottish Fire and Rescue Service in Scotland.
The Responsible Person is required to prevent fire and reduce the risk of death or injury caused by fire. They must ensure that there are suitable means to detect, warn and allow occupants of the building to escape in the event of a fire.
Who Enforces the Regulatory Fire and Safety Order?
The Regulatory Fire and Safety Order is enforced by the Fire and Rescue Service, local authority environment departments or Environmental Health.
The Fire & Rescue Service (FRS) will investigate all fires in Great Britain and ensure that fire safety equipment is working correctly. The FRS also offers advice on how to reduce the risk of fire.
What Does the Responsible Person Need to do?
A Responsible Person must undertake a fire risk assessment for the building, and make sure that the staff know the fire safety procedures. The Responsible Person must also carry out a fire risk assessment at least once every 12 months unless the premises are not open to the public for more than 4 days per week.
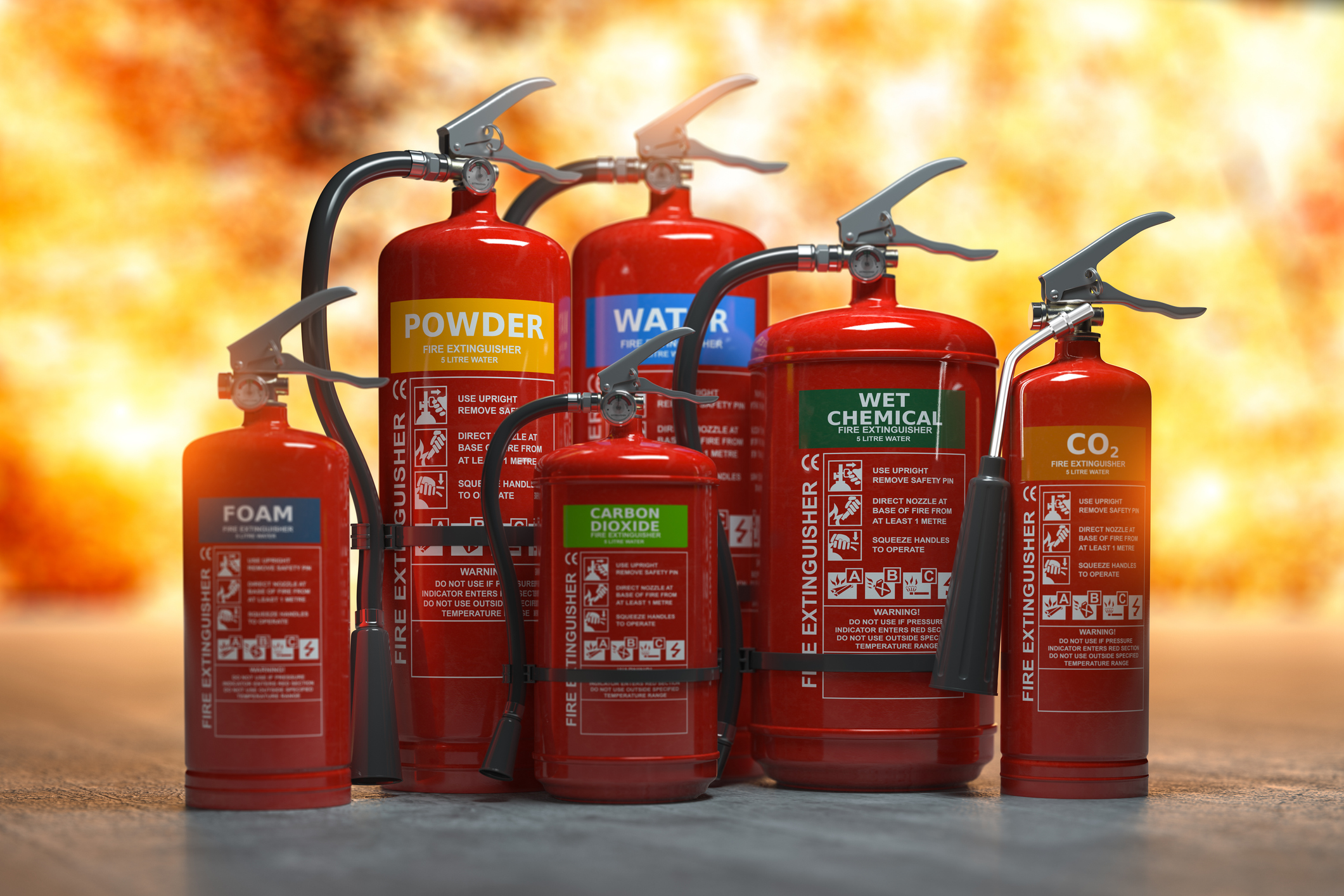
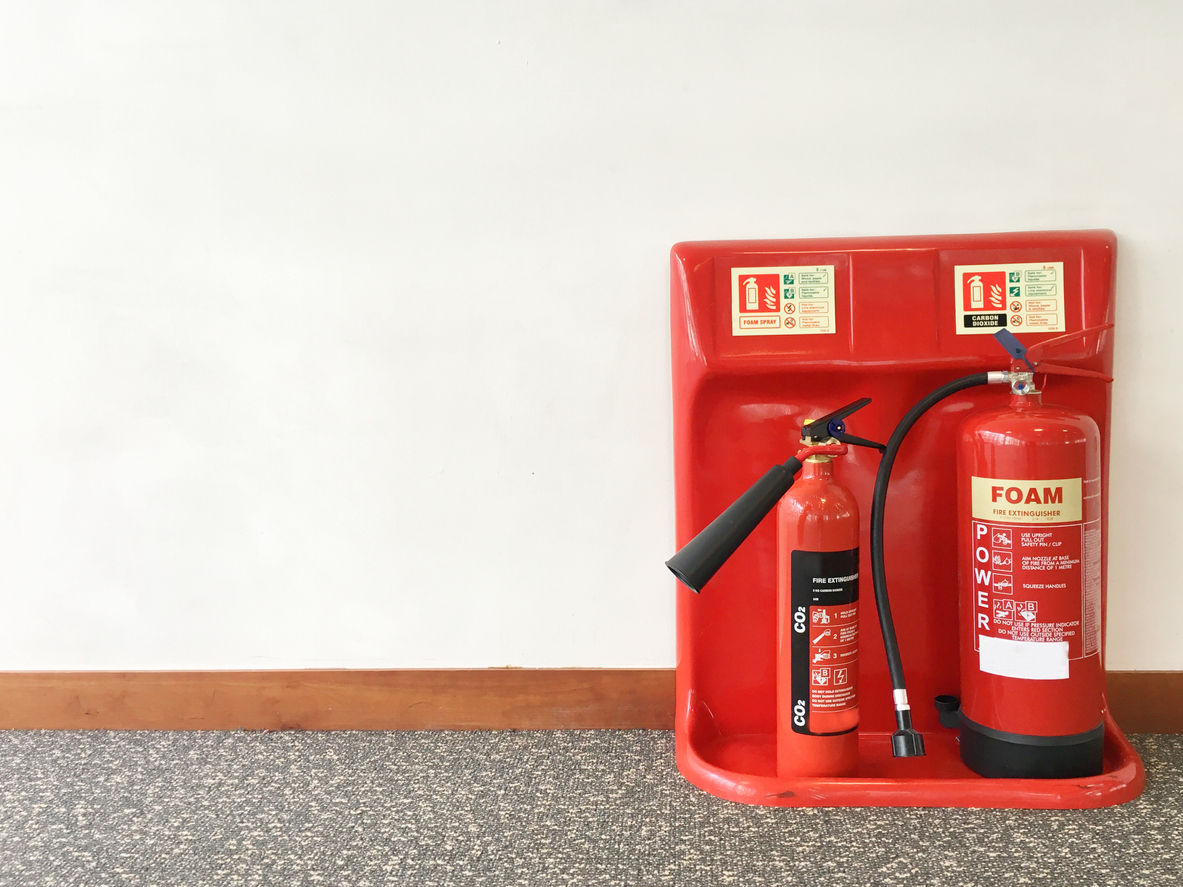
The Responsible Person must ensure that there is an adequate number of appropriate fire extinguishers in places where they can be used safely. It’s good practice to have at least one extinguisher on each floor level in case of a small fire.
It’s also good practice to ensure that all areas with electrical equipment have an electrical circuit breaker installed in case of overheating. Visible signs should be in place, warning individuals not to come into contact with these areas.
Non-Domestic Premises
The following are some establishments considered to be non-domestic premises:
• Offices
• Hospitals and Health Centres
• Schools and Colleges (including Universities)
• Transport Terminals
• Places of Entertainment
The person in charge of non-domestic premises must make sure that it meets fire safety standards at all times including after hours. This can include ensuring that there is an adequate number of fire extinguishers present within the building itself, having sprinkler systems fitted, providing smoke detectors, and preventing the build-up of combustible materials etc.
Shared Premises
Shared premises are premises that are used for a common purpose and include hotels, hostels, hospitals, nursing homes and prisons. They must have a fire risk assessment completed by an appropriate person. The level of risk identified from this assessment must be taken into account when setting up an appropriate fire action plan.
The fire action plan should be reviewed regularly and updated where necessary to ensure it is still fit for purpose. It should also be reviewed after a change in circumstances so that any changes can be incorporated into your written procedures.
The shared premises must have adequate means of escape in case of fire including:
• An exit route which is not obstructed or blocked by lockable doors
• Fire-resistant walls throughout
• Fire-resistant staircases leading directly to the ground floor
• A smoke detection system with audible alarms
Employers’ Duties
An employer has several duties they have to follow. For example:
• Carrying out risk assessments
• Informing staff and representatives of any risks
• Implement and maintain fire safety measures
• Plan for any emergencies
• Provide staff with information and fire safety training
Employees Duties
As an employer, you have to ensure that employees are aware of their responsibilities regarding fire safety. This includes training employees in the following areas:
• How to prevent fires from starting and spreading
• The importance of reporting any potential risks
• How best to deal with fires when they occur
In addition, it’s also important that your staff are aware of the rules on fire safety (particularly if they work with specific equipment or materials). For example, those who work with chemicals should be trained on how these may react under certain conditions.
For more information on responsibility for fire safety, don’t hesitate to get in touch with a member of our team today.